By: Kudakwashe Mugarisanwa
“Land surveyors can spend as much time reading legislation, bylaws, and engineering documents as we spend in front of an instrument in the field or calculating coordinates for a subdivision. We are mathematicians, historians, project managers, advocates, engineers, and even chainsaw operators!” ~ Mark Mason
Table of Contents
Who Is A Surveyor?
A surveyor measures and maps the Earth’s surface, providing essential data for various industries such as construction, real estate, and land development. Surveyors use a combination of tools, including GPS, total stations, and drones, to accurately determine distances, angles, and elevations between points on the land. Their work is vital for establishing property boundaries, creating maps, and supporting the design and construction of infrastructure like roads, buildings, and bridges.
Surveyors often specialize in different types of surveying, such as land surveying, which focuses on determining legal property boundaries; topographic surveying, which maps the contours and features of the land; and construction surveying, which ensures that structures are built according to design specifications. Each specialization requires a keen understanding of both the technical aspects of measurement and the legal implications of land use and ownership. Surveyors frequently collaborate with engineers, architects, and urban planners, providing the foundational data needed for successful project planning and execution.
THE UNSUNG HEROES OF CONSTRUCTION
Role of Surveyors in Construction Projects.
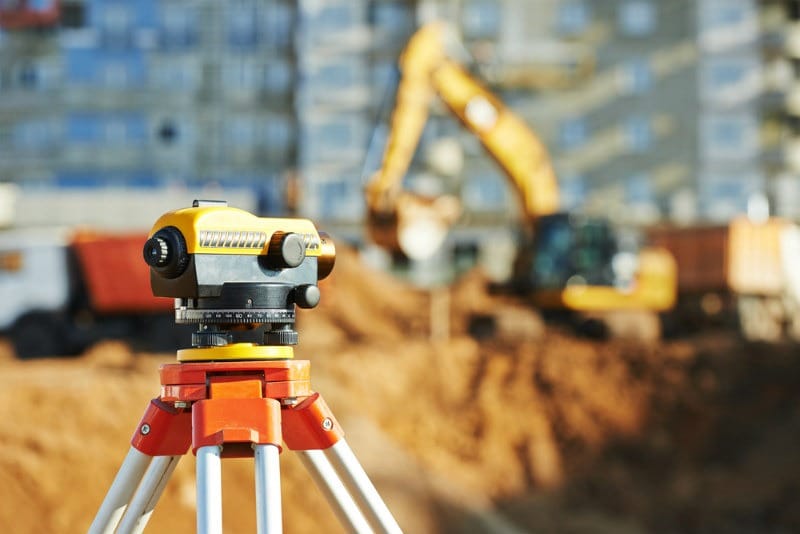
Surveyors play a vital role in construction projects, ensuring that buildings, roads and other infrastructure are constructed accurately and safely, Let’s explore the importance of surveyors in construction projects:
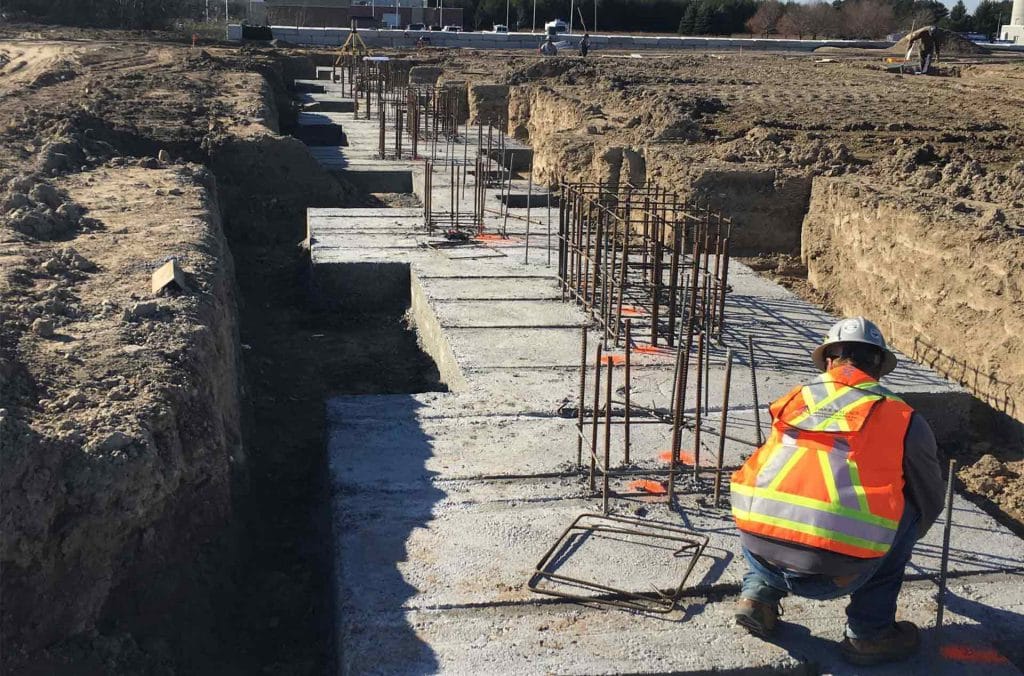

Pre-Construction Surveying
Pre-construction surveying is a critical phase in the construction process that involves detailed assessments and measurements before any actual building begins. This stage ensures that projects are planned accurately, potential issues are identified early, and resources are effectively allocated. Surveyors get to determine property boundaries, topography and existing features.
[time_zone_intelligence]
Types of Pre-Construction Surveys
1. Land Surveys
Land surveys establish property boundaries and identify existing features such as roads, utilities, and topography. They are essential for determining the legal aspects of land use.
2. Topographical Surveys
These surveys map the terrain of the construction site, capturing details about elevation changes, natural features, and existing structures. This information is vital for planning drainage, landscaping, and building foundations.
3. Geotechnical Surveys
Geotechnical surveys assess the soil and subsurface conditions at the site. They provide information on soil composition, stability, and load-bearing capacity, which is crucial for foundation design.
4. Environmental Surveys
Environmental assessments evaluate potential impacts on the surrounding ecosystem. These surveys help identify protected areas, wildlife habitats, and other environmental concerns that must be addressed.
5. Utility Surveys
Utility surveys locate existing underground utilities such as water, gas, electricity, and telecommunications. This information is essential to prevent damage during excavation and construction
6. Layout and Positioning
Layout and positioning are fundamental tasks performed by surveyors during the construction process. These activities ensure that structures are built according to precise specifications, enhancing accuracy and minimizing errors.
Key Responsibilities of Surveyors in Layout and Positioning
1. Setting Out
Surveyors translate design plans into physical markers on the ground. This involves:
- Establishing baseline dimensions.
- Marking corner points and reference lines.
- Ensuring that all elements, such as foundations and walls, align with the design specifications.
2. Measurement and Verification
Surveyors use various tools to measure distances and angles accurately. Techniques include:
- Total Stations: Electronic devices that measure angles and distances, providing precise data for layout.
- GPS Technology: Global Positioning System tools that offer high accuracy for large-scale projects.
- Theodolites: Instruments used for measuring horizontal and vertical angles, crucial for accurate positioning.
3. Site Control
Surveyors create a control network, which consists of permanent reference points that guide construction. This network ensures consistency and precision throughout the project.
4. Monitoring
Surveyors continuously monitor the layout during construction to ensure adherence to plans. This includes:
- Checking for any deviations from the original layout.
- Making adjustments as necessary to maintain accuracy.

5. Risk Management
Yes, it is not only up to project managers or risk managers to look out for risks. Surveyors also identify potential risks and provide solutions to mitigate them. Risk management includes
- Risk identification – Surveyors assess various factors that could pose risks to a project, including: Site Conditions: Evaluating topography, soil stability, and drainage issues, Environmental Factors: Identifying potential impacts on local ecosystems and compliance with environmental regulation, Legal Issues: Ensuring that property boundaries, easements, and zoning laws are clearly understood.
- Risk Assessment – Once risks are identified, surveyors evaluate their potential impact and likelihood. This involves; Quantifying Risks: Assessing the severity of risks and their potential financial implications, Prioritizing Risks: Determining which risks require immediate attention based on their potential impact on the project.
- Risk Mitigation Strategies – Surveyors develop strategies to mitigate identified risks, including: Design Modifications: Adjusting plans to address site-specific challenges, such as modifying foundation designs based on soil conditions. Monitoring: Implementing ongoing assessments to track potential risks throughout the project lifecycle. Communication: Keeping stakeholders informed about risks and mitigation strategies to ensure collaborative problem-solving.
- Compliance and Documentation – Surveyors ensure that all risk management strategies comply with local regulations and standards. This includes: Maintaining Records: Documenting risk assessments, mitigation measures, and compliance efforts. Reporting: Providing regular updates to project managers and stakeholders about risk status and any changes.
Therefore, surveyors are integral to the success of construction projects. Their expertise in land measurement, cost estimation, and project management ensures that projects are executed efficiently and accurately. As construction methods and technologies evolve, the role of surveyors will continue to adapt, making them indispensable in the industry. Understanding their contributions can help stakeholders appreciate the complexities of construction and the importance of professional surveying.













